
/PeriodicTableOxidation-BW-56a12da83df78cf772682bfe.png)
I n peroxides (O 2 – ), oxygen has oxidation number –1 in superoxides (O 2 2– ), oxygen has oxidation number –1/2 and in OF 2, the oxygen has an oxidation number +2. It shows an oxidation state of -2 in almost all the compounds excepts seroxides and superoxides, Oxygen after fluorine is the second most electronegative element. Oxidation number of any element in its elementary state is zero.įluorine is the most electronegative element. In case of an ion, the algebraic sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms is equal to the charge on the ion, The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in an uncharged compound is zero. The resulting charges on the various atoms when the bonding electrons are so assigned are the oxidation numbers of the atoms. Or, if the two atoms are alike, the shared pair is split between the two, one electron being assigned to each atom. In doing this, a shared pair or electrons between two atoms is assigned to the atom with the greater electronegativity. The oxidation number for an element in a covalent compound is by taking the oxidation number to be equal to the charge that the element would carry, if all the bonds in the compound were regarded as ionic instead of covalent. For simple ions, the oxidation number is equal to the ionic charge, e.g. Similarly, the Cu 2+ and Al 3+ ions have oxidation numbers of +2 and +3, whilst F - and O 2- have oxidation numbers of - 1 and - 2. When sodium, for example, is oxidised it loses one electron, and the Na + ion is said to have an oxidation number of +1. The oxidation state or oxidation number of an element is the number of electrons it might be considered to have lost or gained.Īll elements in the elementary, uncombined state are given oxidation numbers of zero. When an element is oxidised it must be acting as a reducing agent and it, therefore, loses electrons when reduced, it gains electrons. Concepts of Physics by HC Verma for JEE.IIT JEE Coaching For Foundation Classes.Of the periodic table, and the 6th and 7th periods.
Oxidation number of all elements in periodic table series#
One of the lanthanide series elements and most of the actinide series elements are synthetic (human-made). They are made up of the lanthanide and actinide series. Also, all noble gases have 8Įlectrons in their outer shell which makes them very stable. This keeps them from making compounds easily. Group 17 includes the halogens and are five non-metallicĮlectrons in their outer shells and an oxidation number of -1. They are very brittle, can be a gas (oxygen) or a solid (carbon), have no metallic luster, do not reflect light and have oxidation numbers of +/-4, -3, & -2. They are not able to conduct heat ore electricity well. Metalloids, such as silicon and germanium, are semi-conductors. They have properties of both metals and non-metals. Their oxidation numbers are +3, +/14, and -3.īetween the metals and non-metals along a boundary. They are solid, have high density, and are opaque. They do not exhibit a variety of oxidation states, they have valence electrons only in the outer shells.
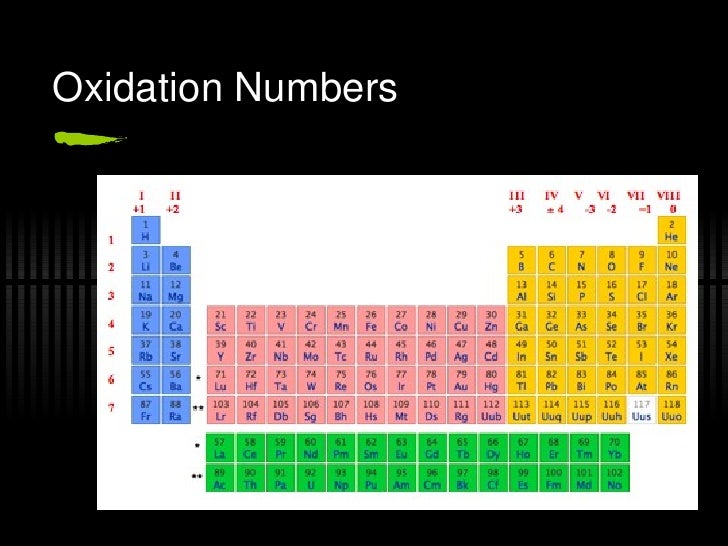
They are malleable and ductile but are not the same as transition elements. Groups 13, 14, & 15 include the other metals elements. They have valence electrons in more than one shell and exhibit several common oxidation states. They are malleable and ductile and also conduct heat and electricity. Groups 3 through 12 include 38 elements called transition metals. Metallic elements and have an oxidation number of +2, making them very Group 2 includes the alkaline earth elements. They are malleable, ductile, are good conductors of heat and electricity and are softer than most metals. They have just one electron in their outer shell, and they are ready to lose it in ionic bonding with other elements. They are highly reactive and do not occur freely in nature. Group 1 of the periodic table are the alkali metals. The Periodic table can be divided into nine families of elements each having similar properties. This Periodic Table shows that there is nine different families some example are the Non metals and Alkali Metals and so forth down the line, as seen on the image to the side.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
